ATES System Evaluation and Retrocommissioning
Stockton University is an innovator in sustainable heating and cooling using geothermal applications at their campus in New Jersey. Stockton’s 1400 ton, 400-bore closed-loop geothermal system was one of the largest geothermal HVAC installations in the world when it was constructed in 1994, and it has served Stockton for over 20 years now. Stockton’s Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage (ATES) system was constructed in 2007 and was also a first of its kind in the US. Stockton’s ATES system was designed to provide 800 tons of cooling capacity using six ATES wells at a maximum aggregate pumping rate of 1200 gpm. The system is used for cooling only, and the cold store is charged during winter using a cooling tower to reject heat from the warm wells.
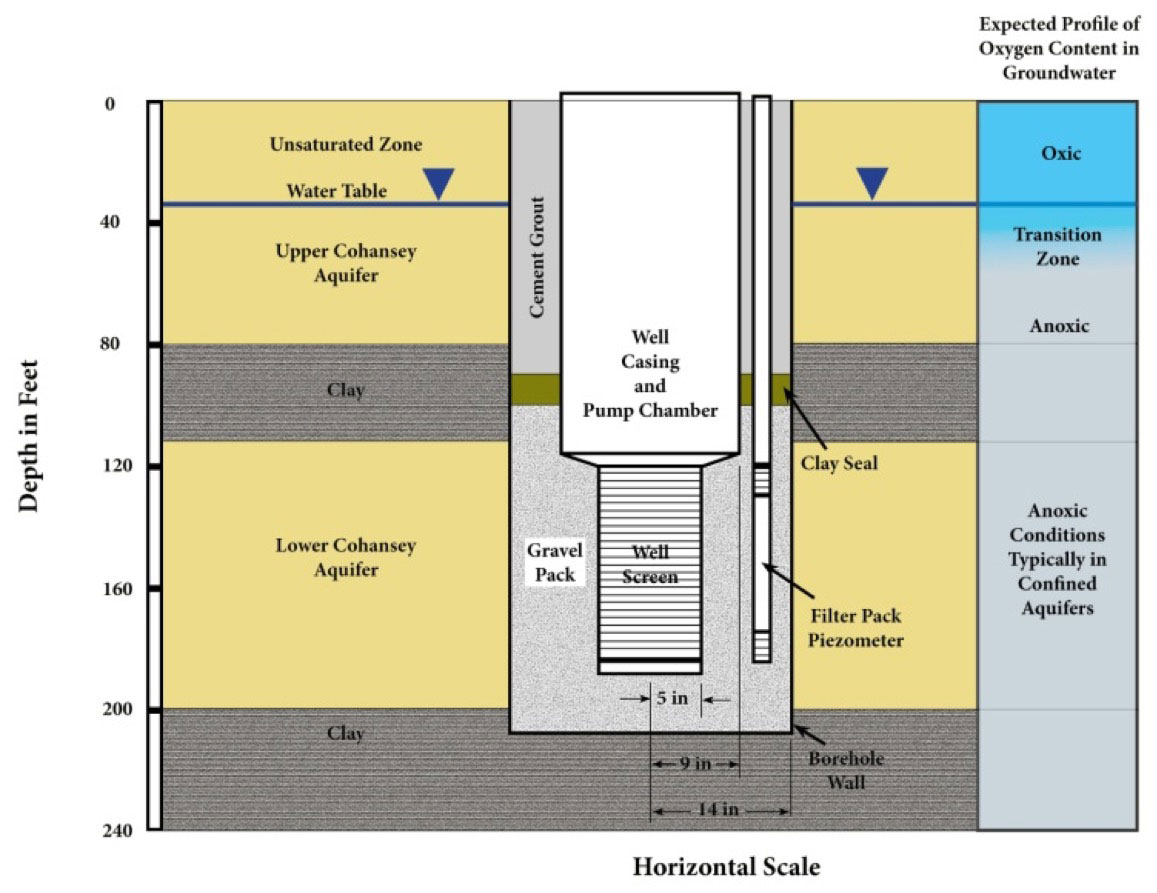
Stockton’s ATES system wells are about 190 feet deep and completed in the lower Cohansey aquifer in the coastal plain of New Jersey. The three warm wells are separated from the three cold wells by about 700 feet.
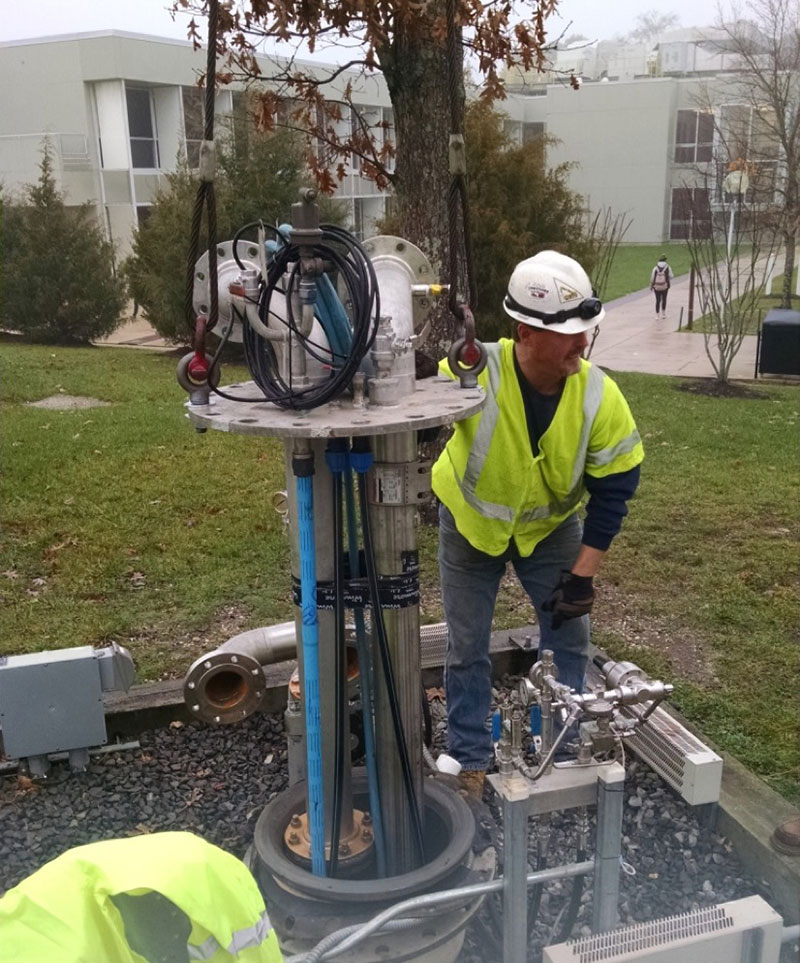
Stockton contracted with Underground Energy to evaluate the performance of the ATES system. Underground Energy teamed with IF Technology, BV, the Dutch ATES specialty firm that designed Stockton’s system. Our work involved data review, site visits, controls testing, and collection and analysis of hydraulic and geochemical data. We also evaluated the how the ATES system is connected to the buildings and design coil temperatures vs. actual in the air handlers. In 2016 we assisted Stockton with ATES well maintenance tasks including replacement of a roll-seal valve in one of the ATES wells, which required hoisting the 100-foot long pump string from the well.